Abstract:Discover how the forex trading spread impacts your profits, expert tactics to minimize spread losses, and how to identify hidden costs in forex trading.

Introduction
The world of forex trading is exhilarating, fast-paced, and promises significant rewards for those who understand its intricacies. Among the critical factors influencing a traders success is the forex trading spread—the seemingly modest gap between the buy and sell price of a currency pair. While often overlooked by novices, the spread quietly shapes winning and losing trades, determines cost structures, and ultimately affects your bottom line. In 2025, shifting market volatility, regulatory changes, and technological advances make mastering the spread more essential than ever.
Whether you are a seasoned trader or just starting, understanding the latest dynamics of forex spreads is fundamental. This article breaks down the impact of spreads on profits, proven ways to trim losses, and the not-so-obvious costs every trader should watch for.
Understanding the Impact of Spread on Profits
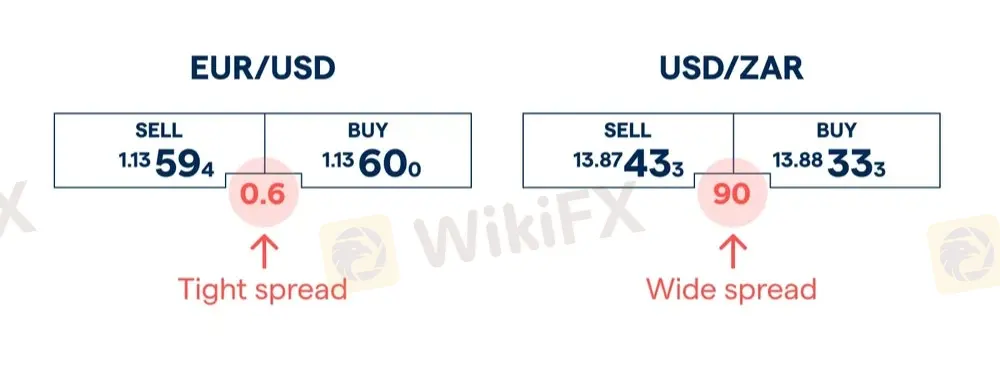
At its core, the forex trading spread is the difference between the bid (the price buyers are willing to pay) and the ask (the price sellers are asking) for a currency pair. This modest difference acts as the primary transaction cost in most forex trades and is measured in pips—the smallest price movement in the forex market.
How Spread Influences Your Trade
The spread represents an immediate “hurdle” for your trade. For example, if the EUR/USD has a 2-pip spread, your trade begins 2 pips in the negative; you must clear this gap in your favor before realizing any profit. On high-frequency and large-volume trades, these costs accumulate quickly and can drain profitability over time.
- Low spreads = higher profits: Tighter spreads reduce your entry cost and increase the share of potential profit you retain.
- High spreads = higher hurdle: Wider spreads demand more significant price movement for you to break even, affecting both scalpers and long-term traders.
What Determines Spread Size?
Several factors shape the spread on any given currency pair:
- Liquidity: Major pairs like EUR/USD offer tighter spreads due to high trading volume, while exotic pairs have wider spreads.
- Market Volatility: During economic announcements or market shocks, spreads can widen suddenly, increasing your risk and trading costs.
- Broker Type: ECN (Electronic Communication Network) brokers usually provide variable, tighter spreads compared to market makers, offering fixed, often wider spreads.
- Trading Hours: During peak sessions—especially when major financial markets overlap—liquidity is abundant, and spreads tend to shrink.
Example: Spreads Real-World Cost
Suppose you‘re a day trader opening ten positions daily, with an average spread cost of 1 pip per trade on a 0.10 lot size. In a month, that’s 220 pips or around $220 eaten by spreads alone. If your net profit is $500, almost half is lost to the spread. Halving that cost instantly boosts your profit margin.
Are Spreads More Important for Certain Strategies?
Yes. Scalpers and active day traders, executing many trades with small targets, feel the sting of spreads more than swing or position traders. High-frequency trading amplifies the costs—or savings—from spread negotiation and selection.
Tactics to Minimize Spread Losses
Given the spreads outsized influence, smart traders deploy a range of tactics to reduce spread drag and maximize trading efficiency.
1. Choose the Right Broker
Not all brokers are created equal. Compare and select brokers with a reputation for tight spreads, fast execution, and transparent pricing. ECN and STP (Straight Through Processing) brokers typically offer raw interbank spreads with a separate commission, which can be more cost-effective for active traders.
2. Focus on Major Currency Pairs
Major pairs (EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY) consistently enjoy the smallest spreads due to their liquidity. Stick with them to minimize trading costs, especially if you are new to forex.
3. Trade During Peak Market Hours
Spreads contract when markets are liquid. The overlap of London and New York sessions is a particularly favorable time for tight spreads and lower trading costs. Avoid trading during off-hours or just before and after major economic news, as spreads can widen unpredictably.
4. Utilize Limit Orders and Spread Indicators
Avoid market orders, especially during volatile times. Limit orders give you more control over entry price and can help you sidestep sudden spread spikes. Use spread indicators available on advanced trading platforms to monitor real-time changes and wait for advantageous moments to enter or exit trades.
5. Consider Fixed vs. Variable Spread Accounts
- Fixed Spreads: Offer price stability, especially useful in high-volatility periods, but tend to be wider overall.
- Variable Spreads: Automatically adjust to market conditions. Cheaper when liquidity is high, potentially riskier during adverse events.
Evaluate which model aligns best with your trading style and risk tolerance.
6. Keep an Eye on Hidden Broker Fees
Some brokers advertise tight spreads but recoup costs through commissions, slippage, and withdrawal fees. Always clarify the full fee schedule before committing.
7. Leverage Technology and Stay Informed
AI-powered trading tools, increasingly indispensable in 2025, can help monitor spreads, execute trades at optimal times, and alert you to widening spreads. Staying informed about central bank decisions, regulatory changes, and macroeconomic events also arms you with knowledge to anticipate and mitigate spread risks.
Access the real time spread comparison here: https://www.wikifx.com/en/spread.html
Spotting Hidden Costs in Forex Trading Spread
Beyond the visible transaction cost of the spread, a web of hidden expenses can erode profits if ignored. These include:
1. Commissions
While some brokers offer zero-commission trading, others add a per-trade fee on top of the spread—particularly with ECN-style accounts. This can be worthwhile for extremely tight spreads, but must be factored into your total cost per trade.
2. Swap (Overnight Financing Fees)
Holding positions overnight may result in swap charges—interest payments based on the difference between the two currencies underlying interest rates. Swap fees can be significant for long-term traders and often vary by broker and currency. If you are trading for multiple days, compare swap rates across brokers.
3. Slippage
Slippage happens when your trade is executed at a different price than intended, commonly during volatile market conditions. This “hidden” cost can turn a tight spread into a costly transaction. Limit orders and advanced trading algorithm usage can reduce slippage risk.
4. Requotes and Order Delays
Especially with certain market makers, you might experience requotes—where the broker offers a new price when executing your order. These delays can force you into less favorable spreads unexpectedly.
5. Withdrawal and Deposit Fees
Some brokers offset their low-spread promise with fees related to account funding, withdrawal, or currency conversion. Always read the fine print to identify these hidden costs.
6. Regulatory and Platform Fees
With new forex regulations tightening oversight in 2025, some brokers pass on the administrative costs as increased fees or minimum trade sizes. Use only brokers regulated by reputable authorities for transparent practices and additional protection.
Conclusion
The forex trading spread is much more than a minor technicality; it is an ever-present cost that can either propel or derail your trading performance. In 2025s dynamic market, staying competitive means internalizing the direct and indirect effects of spreads—including selecting the right broker, timing trades, prioritizing low-cost pairs, and staying vigilant for hidden fees.
By deploying proven tactics to minimize spread losses and carefully scouting for less obvious trading costs, both new and experienced traders can retain more of their profit and avoid the common pitfalls that quietly eat away at trading capital. Remember: in a market where every pip counts, mastering the spread is not just smart; it is essential for long-term success.